Which Body System Controls Body Processes And Functions Through Electrical Impulses?
Body arrangement communication
Page Content
This focus idea is explored through:
- Contrasting student and scientific views
- Disquisitional teaching ideas
- Teaching activities
- Farther resource
Contrasting student and scientific views
Student everyday experiences
Students volition be aware that their body responds to changes in the environment (for example, through heat regulation), merely may be dislocated well-nigh what causes these responses and how they occur. They may not be aware of the man torso's 2 important communication systems, the nervous system and the endocrine (hormone) organisation.
Students may focus on nerves with particular attending to their feelings, merely may non consider them in relation to how the torso responds to the surround (internal and external). They do realise the speed with which nerves operate with respect to their feelings, for example the speed with which happiness can modify to sadness or anger. Students are likewise often unaware or confused near the nervous organization equally a whole and the relationship that exists between the different parts of the nervous organisation (the brain, spinal cord and fretfulness).
Research: Driver (1994)
The human torso responds to hormones in a sustained, widespread style. Students will take heard about hormones (especially in relation to pimples and the contraceptive pill), only they are likely to be dislocated about how they role. Their everyday experiences may hateful that some students are more familiar with certain hormone functions (such as diabetics), than others (such as happiness equally a result of the actions of endorphins).
Students often hear nearly hormones in the media. For example, they may have heard that chickens are fed hormones and that when humans swallow these chickens they are affected in different means, such as faster maturation of children. However, students have little noesis of how this may occur. They may also have heard nearly the utilize of growth hormone by athletes, though they are likely to be confused about its source or the details of its role.
Inquiry: Driver (1994)
Scientific view
Humans have two types of advice systems. These are the nervous arrangement and the endocrine (hormone) system. These systems regulate body processes through chemical and electrical signals that laissez passer between cells. The pathways for this communication are different for each system.
Research: Evans, Ladiges, McKenzie, Batterham & Sanders (2007)
Responses triggered by hormones are generally slower and more than sustained than the responses of the nervous organisation which are targeted and short lived. Responses of the hormone system impact cells that are likely to exist widely distributed throughout the body, such equally the hormones involved in sexual maturation, whereas the actions of nerves are likely to be more targeted.
Further information may exist sourced from the University of Washington: Neuroscience for Kids.
Critical teaching ideas
- The nervous and endocrine systems are two forms of advice arrangement in the human being body that integrate, coordinate and reply to sensory information which is received by the man body from its environment.
- In both the nervous and the endocrine arrangement signals are passed from ane prison cell to another by chemical communication.
- In the nervous organisation, nerve cells send messages electrochemically: this means that chemicals cause an electrical impulse from 1 jail cell to another. This response is targeted and short lived. In the endocrine organisation, glands secrete hormones into the blood that travel to the target organs to effect a more widespread and sustained response.
![]() Explore the relationships between ideas about torso system communication in the Concept Evolution Maps – (Cell Functions, Cells and Organs)
Explore the relationships between ideas about torso system communication in the Concept Evolution Maps – (Cell Functions, Cells and Organs)
Teaching activities
Clarify and consolidate ideas for/by advice to others
Students compare and contrast the nervous and endocrine systems with each other and other everyday communication systems that they are used to dealing with.
a) Students write a research report comparing and contrasting wireless engineering (computer systems) with the hormone and nervous arrangement. They should expect specifically at the speed of response and the information carried.
b) Students relate the human communication systems (nervous and hormone) to communication systems in order and the technology that is used (such as mobile phones and landline telephones) and brand comparisons between them.
Promote reflection on and clarification of existing ideas
Teachers should allow students to experience and build their knowledge by experimenting, researching and modelling.
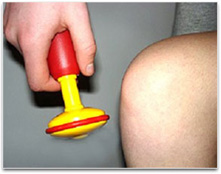 a) Students work in pairs to test reflexes (nerve responses). It is best to test rapid nervus responses (which are particularly needed in case of danger). These responses include reflex responses in the knee and of the eye pupil to light. To extend this part of the activity students can investigate whether these responses tin exist prevented.
a) Students work in pairs to test reflexes (nerve responses). It is best to test rapid nervus responses (which are particularly needed in case of danger). These responses include reflex responses in the knee and of the eye pupil to light. To extend this part of the activity students can investigate whether these responses tin exist prevented.
Research: Lewis (1999)
b) Endocrine (hormonal) responses are much slower and sustained for longer. To explore the endocrine system students tin produce a large display of the hormone arrangement. Using a large piece of paper, they should draw an outline of a student and fix it to the wall. Students then research information on unlike glands and the role of the hormones they produce. They draw pictures of the glands, stick each picture to the body outline and attach data about the hormone that is produced. This activeness could be extended by researching information on weather created by besides depression or as well high levels of hormones.
Inquiry: Lewis (1999)
Further resources
Science related interactive learning objects can be found on the FUSE Teacher Resources folio.
To access the interactive learning object below, teachers must login to FUSE and search by Learning Resource ID:
- Body Parts: endocrine organisation – students expect closely at the homo endocrine system. They learn what hormones are and which glands release them. They find out which glands regulate bodily functions such as energy levels, digestion, calcium levels, growth and puberty.
Learning Resources ID: NZGVA3
Which Body System Controls Body Processes And Functions Through Electrical Impulses?,
Source: https://www.education.vic.gov.au/school/teachers/teachingresources/discipline/science/continuum/Pages/bodysystem.aspx
Posted by: huntgony1998.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Body System Controls Body Processes And Functions Through Electrical Impulses?"
Post a Comment